Weight Management in Dogs
 Cecilie Hemsen Berg
Cecilie Hemsen Berg
Obesity is a growing concern for pet owners, with weight gain being the most common preventable disease among dogs. Even slight weight gain can significantly reduce a dog’s lifespan and increase the risk of severe health problems. A study on Labrador Retrievers showed that being even moderately overweight could shorten a dog’s life by nearly two years compared to leaner dogs. This blog explores the causes, identification, health risks, and prevention strategies for obesity in dogs.

Causes of Weight Gain
Obesity in dogs is primarily a lifestyle disease, influenced by diet, exercise, and other factors. While it is usually easy to prevent and treat, understanding the root causes is crucial:
- Overfeeding and Excessive Treats: Many dog owners use food as a reward or a way to express love, but overfeeding, especially with high-calorie treats, can lead to weight gain. Portion control is essential.
- Lack of Exercise: Regular exercise is vital for a dog’s health. Different breeds have varying exercise needs. For example, active breeds like Border Collies require more physical activity than smaller toy breeds, which may only need 30 minutes of exercise daily.
- Unbalanced Diet: A diet high in fat, calories, or inappropriate for the dog’s age can contribute to weight gain. Puppies, adults, and senior dogs all have different nutritional needs.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like hypothyroidism, hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing’s disease), and joint pain can lead to decreased activity and weight gain.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as those for contraceptive management, can increase the risk of obesity.
- Breed Predisposition: Some breeds are more prone to obesity, such as Labrador Retrievers, Collies, and Basset Hounds.
Factors Contributing to Weight Gain
In addition to the primary causes, several other factors can increase a dog’s risk of becoming overweight:

- Gender: Female dogs are more likely to gain weight than males.
- Age: Older dogs have slower metabolisms, making them more susceptible to weight gain.
- Early Weight Issues: Overweight puppies are more likely to have weight problems in adulthood.
- Neutering/Spaying: Neutered or spayed dogs may require up to 20% fewer calories due to hormonal changes affecting metabolism.
- Joint Pain: Dogs with joint issues may be less active, increasing the risk of weight gain.
How to See if your Dog is Overweight
Knowing whether your dog is overweight or obese is the first step in managing their weight effectively. Here are some methods to assess your dog’s body condition:
Body shape
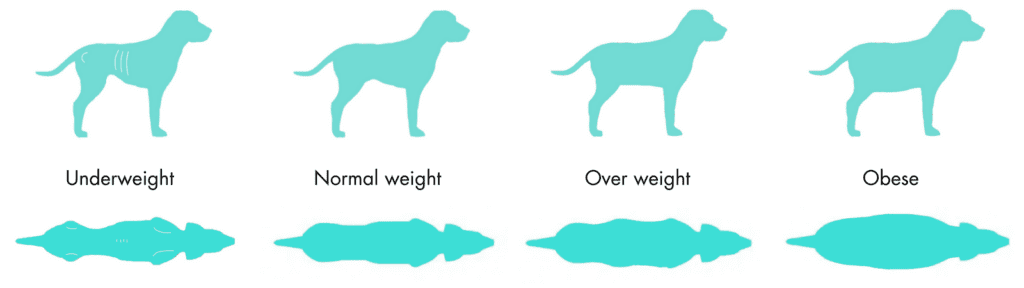
To quickly determine if your dog is overweight, start by assessing its body shape. Refer to a body condition chart, which illustrates various dog body types ranging from underweight to obese. When viewing your dog from the side, a healthy weight is indicated by a tucked-up tummy and a lean body where you can easily feel the ribs without them being visible. When looking from above, your dog should have a defined waist and a slightly tapered shape from the shoulders to the hips. However, if you can see prominent bones, this may indicate your dog is underweight, which is also unhealthy and requires attention.
Weight
You can do a quick Google search to find the average weight of your dog’s breed and sex. Your vet can also tell you what weight is ideal for your dog, based on sex, breed and age. If your dog is between 10% to 15% over its ideal weight, it is classified as obese. If your dog is obese, ideally, your dog should achieve about 1-3% body weight loss per week.
Rib test
Stand behind your dog, and gently run your hands along both sides of the rib cage. You should be able to feel, but not see each rib easily, and your dog should have a waist or a tucked-up area in front of the hind legs. If you can pinch more than an inch and/or your dog no longer has a waist then you should consult your vet to start a weight-loss plan.
Health Risks Linked to Excess Weight
Obesity in dogs is more than just a cosmetic issue—it poses serious risks to their overall health and well-being. Just like in humans, excess weight in dogs can lead to a cascade of health problems, many of which can significantly shorten their lifespan and reduce their quality of life. Below are some of the most common and severe health issues associated with obesity in dogs.
Reduced Mobility and Grooming Ability: Excess weight can make it difficult for dogs to move comfortably and groom themselves properly.
Breathing Difficulties: This is particularly an issue for short-nosed or brachycephalic breeds like Pugs and Bulldogs.
Shortened Lifespan: Overweight dogs generally have shorter lifespans and may suffer from a reduced quality of life due to various health problems.
Chronic Diseases: Obesity is linked to a range of chronic conditions, including:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Osteoarthritis and joint inflammation
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) and heart disease
- Liver disease
- Chronic kidney disease
- Certain cancers

Strategies to Prevent Unhealthy Weight in Dogs
Preventing obesity is much easier than treating it. Here are some steps you can take:
- Know Your Dog’s Ideal Weight: Consult your veterinarian to determine the optimal weight for your dog based on its breed, age, and sex.
- Provide Balanced Nutrition: Offer a high-quality, balanced diet tailored to your dog’s specific needs. Consider low-calorie options if your dog tends to gain weight easily. For example, Nala Health offers a Senior/Weight Manalement dog food with high-quality protein, Taurine, L-Carnitine, water-soluble fibre, and probiotics to support metabolism and digestive health.
- Portion Control: Use a scale to measure your dog’s food rather than a measuring cup for precise portion control. Adjust food portions if your dog receives treats throughout the day.
- Regular Exercise and Play: Regular physical activity is vital for maintaining a healthy weight. The amount and type of exercise should be suited to your dog’s breed, size, and any existing health issues. Dogs with joint problems or heart disease may benefit from shorter, more frequent walks on soft terrain.

- Limit Treats and Snacks: Treats should be given in moderation and as part of the daily caloric intake. Avoid high-calorie human food and consider healthy alternatives like cucumber or carrots.
- Routine Vet Visits: Regular health checks can help catch early signs of weight gain and associated health issues, allowing for timely intervention.
Nala Health Weight Management Food
Nala Health understands the importance of maintaining a healthy weight for your dog’s overall well-being, which is why we offer a senior/weight management option that is lower in calories. Our premium food contains high-quality protein from black soldier fly larvae (BSFL), helping to support lean muscle mass. In addition to complete protein from BSFL, we have added the amino acids Taurine and L-Carnitine, which play a critical role in the healthy metabolism of fats and heart health, ensuring that your dog efficiently uses stored fat for energy without sacrificing muscle tone.
In addition to its protein content, Nala Health’s Lite dog food contains healthy fibre, which helps to create a feeling of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating and helping to manage calorie intake. The food is also low GI, providing sustained energy through the day. The inclusion of probiotics further supports a balanced gut microbiome, which is crucial for overall health, better digestion, and nutrient absorption. A healthy gut not only aids in digestion but also strengthens the immune system, promotes better skin and coat health, and reduces inflammation.

The carefully selected ingredients in Nala Health’s weight management formula are designed to provide balanced nutrition without excess calories. It is ideal for dogs prone to weight gain, older dogs with slower metabolisms, and those recovering from illnesses or on restricted activity levels. By choosing Nala Health’s weight management food, you can help your dog maintain a healthy weight, reduce the risk of obesity-related health issues, and ensure they stay active and vibrant throughout their life.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy weight for your dog is essential for their overall well-being and longevity. By providing a balanced diet, ensuring regular exercise, and monitoring their weight, you can help your dog live a healthier, happier, and longer life. Remember, managing your dog’s weight requires commitment and sometimes a bit of tough love, but the rewards are worth it.

